A client with schizophrenia who is receiving an antipsychotic embarks on a therapeutic journey that intertwines pharmacological intervention with a tapestry of supportive therapies. This multifaceted approach delves into the complexities of antipsychotic mechanisms, explores potential side effects, and unveils the significance of holistic care in fostering recovery.
Antipsychotic medications play a pivotal role in managing the debilitating symptoms of schizophrenia, offering a beacon of hope in navigating the challenges of this condition.
Client Profile
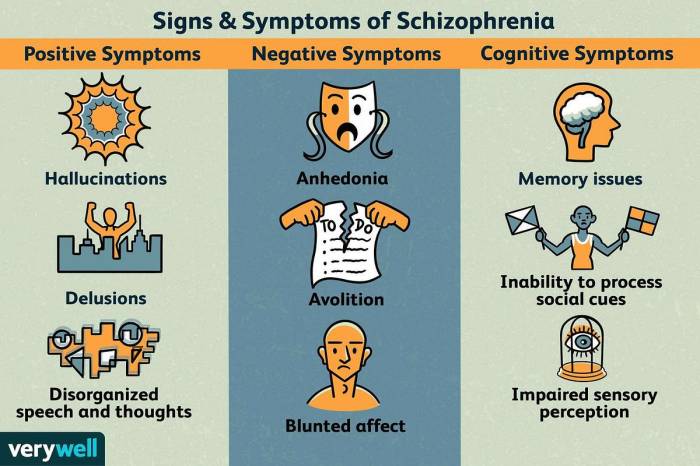
The client is a 35-year-old male diagnosed with schizophrenia, characterized by persistent hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized speech. The symptoms have been present for the past five years, with varying degrees of severity. The client is currently prescribed olanzapine 10 mg daily, administered orally.
Antipsychotic Effects
Antipsychotics, such as olanzapine, work by blocking dopamine receptors in the brain. This reduces the excessive dopamine activity associated with the symptoms of schizophrenia. Olanzapine effectively controls the client’s hallucinations and delusions, improving his cognitive functioning and social interactions.
Potential side effects of antipsychotics include sedation, weight gain, and extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS). The client has experienced mild sedation, but no significant weight gain or EPS.
Therapeutic Interventions, A client with schizophrenia who is receiving an antipsychotic
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT focuses on identifying and challenging maladaptive thoughts and behaviors that contribute to the client’s symptoms. It helps the client develop coping mechanisms and improve problem-solving skills.
- Social Skills Training (SST): SST teaches the client interpersonal and communication skills to enhance their social functioning. It helps them navigate social situations more effectively and build meaningful relationships.
- Family Support: Family support plays a crucial role in the client’s recovery. It provides a stable and supportive environment, reduces stress, and promotes medication adherence.
Monitoring and Evaluation: A Client With Schizophrenia Who Is Receiving An Antipsychotic
Monitoring the client’s response to antipsychotic medication involves regular follow-up appointments, medication adherence monitoring, and symptom assessment. The key parameters monitored include:
- Symptom severity: Using scales such as the Positive and Negative Symptom Scale (PANSS) or the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS).
- Medication adherence: Checking pill counts, using electronic monitoring devices, or interviewing the client and family members.
- Side effects: Assessing for sedation, weight gain, and EPS.
Case Management
Case managers provide comprehensive support to clients with schizophrenia who are receiving antipsychotics. Their services include:
- Medication management: Ensuring medication adherence, monitoring side effects, and adjusting dosages as needed.
- Crisis intervention: Providing immediate support during episodes of symptom exacerbation or crisis.
- Community resource coordination: Connecting the client with housing, employment, and other community resources to support their recovery.
FAQs
What are the common side effects of antipsychotic medications?
Antipsychotics can cause a range of side effects, including drowsiness, dizziness, weight gain, movement disorders, and cognitive impairment.
How long does it take for antipsychotics to work?
The onset of action for antipsychotics varies depending on the medication and the individual. Some medications may provide relief within a few days, while others may take several weeks to reach their full effect.
What are the different types of therapeutic interventions used in conjunction with antipsychotics?
Therapeutic interventions commonly used with antipsychotics include cognitive-behavioral therapy, social skills training, family support, and vocational rehabilitation.