Practice types of cellular transport answer key – Cellular transport is the movement of molecules across cell membranes, and it is essential for a variety of cellular functions. This answer key provides a comprehensive overview of the different types of cellular transport, including passive transport, active transport, and bulk transport.
Passive transport is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This type of transport does not require energy, and it includes processes such as diffusion and osmosis. Active transport is the movement of molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration.
This type of transport requires energy, and it includes processes such as facilitated diffusion and active transport. Bulk transport is the movement of large molecules or particles across cell membranes. This type of transport includes processes such as endocytosis and exocytosis.
Cellular Transport
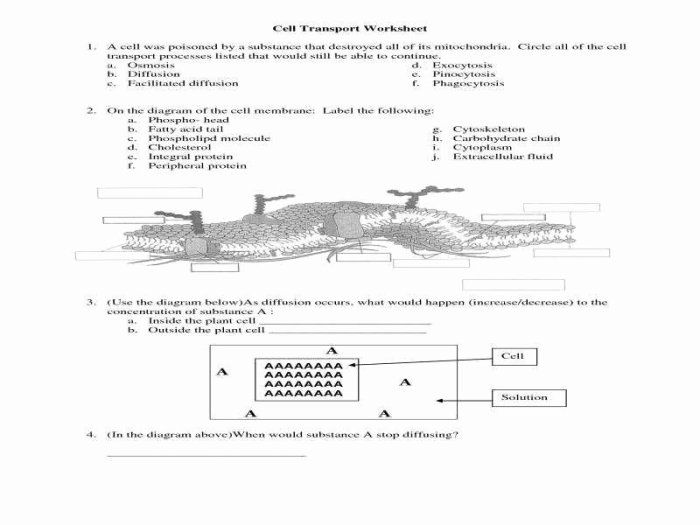
Cellular transport refers to the movement of molecules across the plasma membrane of cells. It is essential for cellular function, as it allows cells to take in nutrients, eliminate waste products, and communicate with each other. There are three main types of cellular transport: passive transport, active transport, and bulk transport.
Passive Transport
Passive transport is the movement of molecules across a concentration gradient, from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. It does not require energy input from the cell. There are two main types of passive transport: diffusion and osmosis.
- Diffusionis the movement of individual molecules across a concentration gradient. It occurs when there is a difference in the concentration of a substance on either side of a membrane. Molecules move from the area of high concentration to the area of low concentration until equilibrium is reached.
- Osmosisis the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. Water molecules move across the membrane in order to equalize the solute concentration on both sides.
Active Transport, Practice types of cellular transport answer key
Active transport is the movement of molecules across a concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. It requires energy input from the cell. Carrier proteins embedded in the cell membrane facilitate active transport.
These proteins bind to the molecules being transported and move them across the membrane against the concentration gradient.
- Sodium-potassium pumpis an example of active transport. This protein pumps sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell, maintaining the proper balance of these ions across the cell membrane.
- Calcium pumpis another example of active transport. This protein pumps calcium ions out of the cell, maintaining a low concentration of calcium ions in the cytoplasm.
Bulk Transport
Bulk transport is the movement of large molecules or particles across the cell membrane. There are two main types of bulk transport: endocytosis and exocytosis.
- Endocytosisis the process by which the cell takes in large molecules or particles from the extracellular environment. The cell membrane invaginates, forming a vesicle that surrounds the material being taken in. The vesicle then pinches off from the membrane and moves into the cell.
- Exocytosisis the process by which the cell releases large molecules or particles from the cell. The vesicle containing the material being released fuses with the cell membrane, and the material is released into the extracellular environment.
Importance of Cellular Transport
Cellular transport is essential for cellular function. It allows cells to take in nutrients, eliminate waste products, and communicate with each other. Impaired cellular transport can lead to a variety of diseases and conditions, such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and cancer.
Key Questions Answered: Practice Types Of Cellular Transport Answer Key
What are the three main types of cellular transport?
The three main types of cellular transport are passive transport, active transport, and bulk transport.
What is the difference between passive and active transport?
Passive transport does not require energy, while active transport does.
What are some examples of passive transport?
Diffusion and osmosis are two examples of passive transport.
What are some examples of active transport?
Facilitated diffusion and active transport are two examples of active transport.
What are some examples of bulk transport?
Endocytosis and exocytosis are two examples of bulk transport.