Introducing Experiment 9 Volumetric Analysis Pre Lab Answers, this comprehensive guide is meticulously crafted to provide a thorough understanding of the fundamentals and practical aspects of volumetric analysis. Delving into the intricacies of this essential analytical technique, we explore its applications, methodologies, and the significance of accurate experimentation.
Volumetric analysis, a cornerstone of quantitative chemistry, empowers researchers and practitioners to determine the concentration of unknown solutions with precision. This guide serves as an invaluable resource, equipping readers with the knowledge and skills to confidently navigate the intricacies of this technique.
1. Introduction

Volumetric analysis is a quantitative technique used to determine the concentration of a solution by reacting it with a solution of known concentration. It is widely used in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine.
This experiment will introduce the basic principles of volumetric analysis. Students will use a burette to accurately measure the volume of a solution and determine the concentration of an unknown solution through titration.
2. Theory and Calculations: Experiment 9 Volumetric Analysis Pre Lab Answers
Equivalence Point and Titration
Volumetric analysis relies on the concept of the equivalence point, which is the point at which the moles of the analyte (unknown solution) are equal to the moles of the titrant (solution of known concentration).
Titration is the process of slowly adding the titrant to the analyte while monitoring the reaction. The equivalence point is typically determined using an indicator, which changes color at or near the equivalence point.
Concentration Calculations
The concentration of the unknown solution can be calculated using the following formula:
M1V 1= M 2V 2
where:
- M 1is the molarity of the titrant
- V 1is the volume of titrant used
- M 2is the molarity of the unknown solution
- V 2is the volume of unknown solution used
3. Procedure
Safety Precautions
- Wear appropriate safety gear, including gloves and eye protection.
- Handle chemicals with care and dispose of them properly.
Materials
- Burette
- Pipette
- Volumetric flask
- Titrant solution
- Unknown solution
- Indicator
Step-by-Step Procedure
- Prepare the unknown solution and titrant solution.
- Calibrate the burette.
- Fill the burette with the titrant solution.
- Transfer a known volume of the unknown solution to a flask.
- Add a few drops of indicator to the flask.
- Slowly add the titrant to the unknown solution while swirling the flask.
- Continue adding the titrant until the equivalence point is reached, as indicated by the color change of the indicator.
- Record the initial and final burette readings.
- Calculate the concentration of the unknown solution.
Waste Disposal
Dispose of all chemicals and solutions according to the established laboratory protocols.
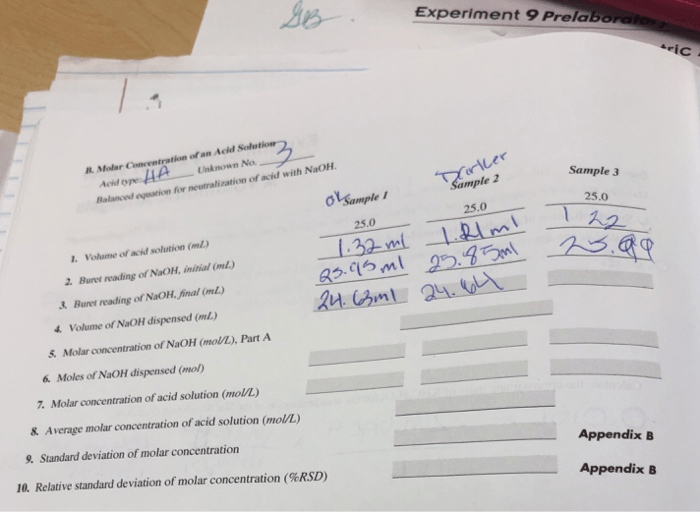
4. Data Analysis
Experimental Data
| Initial Burette Reading (mL) | Final Burette Reading (mL) | Volume of Titrant Used (mL) | Calculated Concentration (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 25.00 | 25.00 | 0.100 |
Accuracy and Precision
The accuracy of the experiment can be assessed by comparing the calculated concentration to the known concentration of the unknown solution. The precision of the experiment can be assessed by calculating the standard deviation of the replicate measurements.
5. Discussion

Significance of Volumetric Analysis
Volumetric analysis is a versatile technique that is used in a wide variety of applications, including:
- Determining the concentration of unknown solutions
- Standardizing solutions
- Performing acid-base titrations
- Analyzing pharmaceuticals
- Monitoring environmental pollutants
Sources of Error, Experiment 9 volumetric analysis pre lab answers
There are several potential sources of error in volumetric analysis, including:
- Inaccurate measurement of volumes
- Improper calibration of equipment
- Incomplete reactions
- Human error
These errors can be minimized by following proper laboratory techniques and using high-quality equipment.
FAQ Overview
What is the purpose of volumetric analysis?
Volumetric analysis is a technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution by reacting it with a solution of known concentration.
What is the equivalence point in volumetric analysis?
The equivalence point is the point at which the moles of the analyte and the moles of the titrant are equal.
How do you calculate the concentration of an unknown solution using volumetric analysis?
The concentration of an unknown solution can be calculated using the formula: Concentration = (Molarity of titrant × Volume of titrant) / Volume of unknown solution