Break up light or sound waves crossword: Embark on a journey to unravel the intriguing world of wave separation, a fundamental concept that has revolutionized our understanding of light and sound. From the captivating effects of refraction to the intricate patterns of diffraction, this discourse delves into the captivating realm of wave manipulation.
Through the prism of scientific inquiry, we will explore how these phenomena have shaped our technological advancements, from spectroscopy in astronomy to ultrasound in medical imaging. Prepare to be illuminated as we trace the historical evolution of wave separation, unraveling the contributions of pioneering scientists and witnessing the transformative power of scientific discovery.
Breaking Up Light Waves
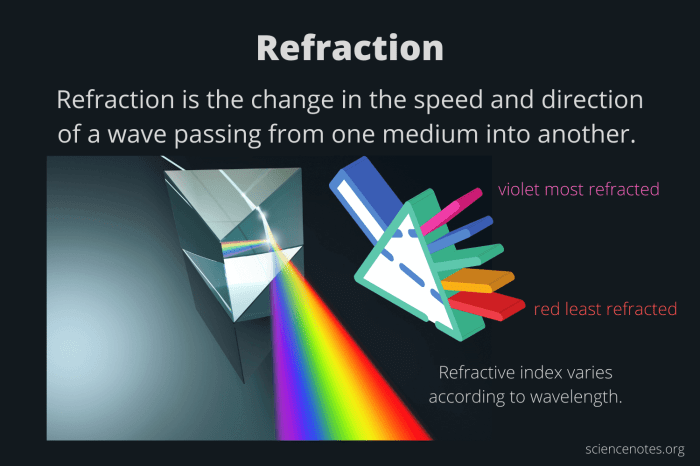
Light waves are electromagnetic waves that travel in a straight line. When light waves encounter an object, they can be reflected, absorbed, or transmitted. The way that light waves interact with an object depends on the object’s properties, such as its shape, size, and composition.
One of the most important properties of light waves is their wavelength. The wavelength of a light wave is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs of the wave. The wavelength of a light wave determines its color. Shorter wavelengths correspond to higher frequencies and blue light, while longer wavelengths correspond to lower frequencies and red light.
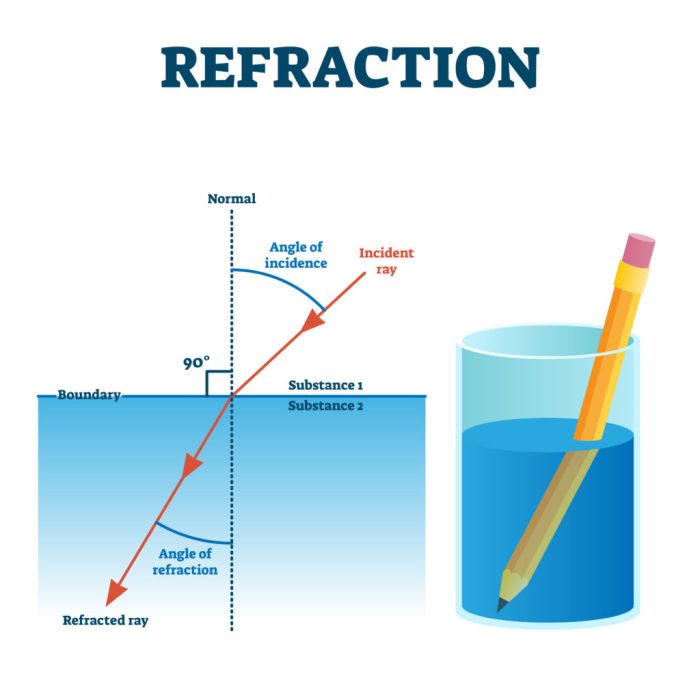
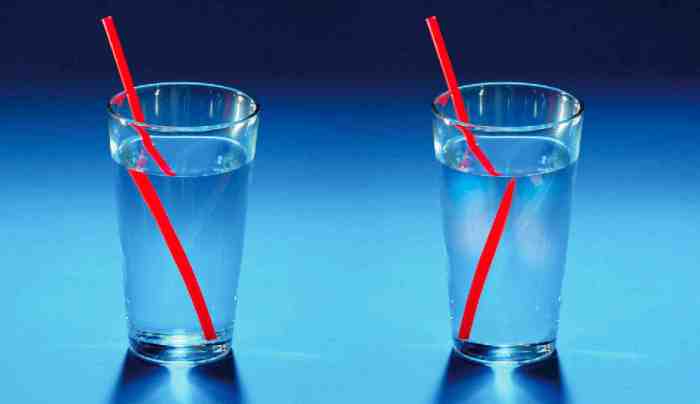
When light waves pass through a prism, they are refracted. Refraction is the bending of light waves as they pass from one medium to another. The amount of refraction depends on the wavelength of the light wave and the difference in refractive index between the two media.
The refractive index of a material is a measure of how much light is bent when it passes through the material. The refractive index of a material is determined by its density and its composition.
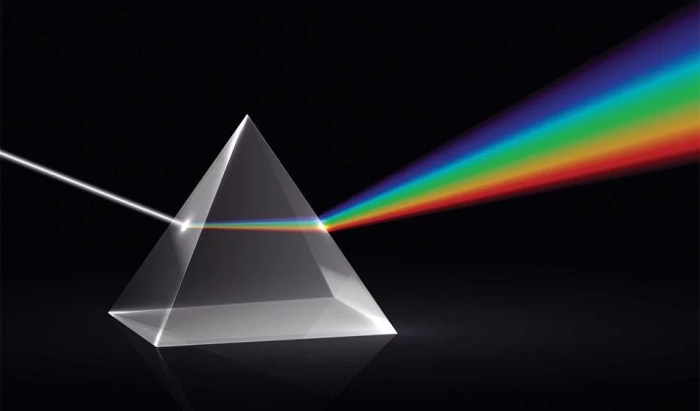
Prisms can be used to separate white light into its component colors. This is because the different wavelengths of light are refracted by different amounts. The shorter wavelengths (blue light) are refracted more than the longer wavelengths (red light). This causes the different wavelengths of light to spread out into a spectrum.
Examples of Refraction in Everyday Life
- The rainbow is caused by the refraction of sunlight as it passes through water droplets in the atmosphere.
- Lenses are used to focus light waves. Lenses can be used to correct vision problems, such as nearsightedness and farsightedness.
- Fiber optics are used to transmit light waves over long distances. Fiber optics are used in telecommunications and in medical imaging.
Breaking Up Sound Waves: Break Up Light Or Sound Waves Crossword
Sound waves are mechanical waves that travel through a medium, such as air, water, or metal. Sound waves are caused by the vibration of an object. The vibration of the object creates a disturbance in the medium, which causes the sound wave to propagate through the medium.
The speed of sound in a medium depends on the density and elasticity of the medium. The speed of sound in air is approximately 343 meters per second. The speed of sound in water is approximately 1,500 meters per second.
The speed of sound in metal is approximately 5,000 meters per second.
Sound waves can be reflected, absorbed, or transmitted. The way that sound waves interact with an object depends on the object’s properties, such as its shape, size, and composition.
One of the most important properties of sound waves is their frequency. The frequency of a sound wave is the number of times per second that the wave repeats itself. The frequency of a sound wave determines its pitch. Higher frequencies correspond to higher pitches, while lower frequencies correspond to lower pitches.
When sound waves pass through a diffraction grating, they are diffracted. Diffraction is the spreading out of sound waves as they pass through an opening or around an obstacle.
Diffraction gratings can be used to separate sound waves of different frequencies. This is because the different frequencies of sound are diffracted by different amounts. The higher frequencies (higher pitches) are diffracted more than the lower frequencies (lower pitches). This causes the different frequencies of sound to spread out into a spectrum.
Examples of Diffraction in Everyday Life, Break up light or sound waves crossword
- The sound of a musical instrument is caused by the diffraction of sound waves as they pass through the instrument’s body.
- Ultrasound is used in medical imaging to create images of the inside of the body. Ultrasound waves are diffracted by the different tissues in the body, which allows doctors to see the different organs and structures.
- Sonar is used to detect objects underwater. Sonar waves are diffracted by the objects in the water, which allows the sonar to determine the location and size of the objects.
Applications of Breaking Up Light and Sound Waves
Breaking up light and sound waves has a wide range of applications in science, technology, and medicine.
One of the most important applications of breaking up light waves is spectroscopy. Spectroscopy is the study of the absorption and emission of light by atoms and molecules. Spectroscopy can be used to identify the elements and molecules that make up a material.
Spectroscopy is also used to study the structure and dynamics of atoms and molecules.
Another important application of breaking up light waves is medical imaging. Medical imaging techniques, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans, use different types of light waves to create images of the inside of the body. These images can be used to diagnose and treat a wide range of medical conditions.
Breaking up sound waves also has a wide range of applications. One of the most important applications of breaking up sound waves is ultrasound. Ultrasound is used in medical imaging to create images of the inside of the body. Ultrasound waves are also used to treat a variety of medical conditions, such as kidney stones and tumors.
Another important application of breaking up sound waves is sonar. Sonar is used to detect objects underwater. Sonar waves are also used to communicate with submarines and other underwater vehicles.
Historical Context

The discovery of refraction and diffraction dates back to the ancient Greeks. In the 3rd century BC, Euclid wrote about the refraction of light in his book Optics. In the 11th century, Ibn al-Haytham wrote about the diffraction of light in his book Kitab al-Manazir (Book of Optics).
In the 17th century, Isaac Newton conducted a series of experiments on the refraction and diffraction of light. Newton’s experiments led to the development of the wave theory of light. The wave theory of light states that light is a wave that travels through a medium.
The wave theory of light was later superseded by the electromagnetic theory of light, which states that light is an electromagnetic wave.
In the 19th century, Augustin-Jean Fresnel conducted a series of experiments on the diffraction of sound waves. Fresnel’s experiments led to the development of the wave theory of sound. The wave theory of sound states that sound is a wave that travels through a medium.
The wave theory of sound was later superseded by the electromagnetic theory of sound, which states that sound is an electromagnetic wave.
Questions and Answers
What is the principle behind refraction?
Refraction occurs when a wave changes speed as it passes from one medium to another, causing it to bend or change direction.
How does a prism separate white light?
A prism separates white light into its component colors because different colors of light refract at different angles.
What is the role of diffraction in sound wave separation?
Diffraction refers to the spreading out of waves as they pass through an aperture or around an obstacle, allowing for the separation of sound waves of different frequencies.