Es claro que subjuntivo o indicativo: Delving into the intricacies of Spanish moods, this comprehensive guide illuminates the nuances that differentiate the subjunctive and indicative moods. Understanding their distinct usage empowers language learners to navigate the complexities of Spanish grammar with confidence and precision.
Embark on a linguistic journey that unravels the purpose, usage, and grammatical cues that guide the appropriate application of each mood. Explore real-life examples that showcase the practical implementation of these concepts, gaining a deeper appreciation for the richness and expressiveness of the Spanish language.
Spanish Subjunctive Mood

The subjunctive mood is a grammatical mood used in Spanish to express uncertainty, doubt, possibility, or emotion. It is typically used in subordinate clauses that depend on a main clause containing a verb that expresses a wish, desire, suggestion, or doubt.
Types of Subjunctive Clauses, Es claro que subjuntivo o indicativo
- Substantive clauses:Function as nouns and can be used as subjects, objects, or complements.
- Adjective clauses:Modify nouns and provide additional information.
- Adverbial clauses:Express a variety of relationships, such as purpose, cause, or condition.
Spanish Indicative Mood: Es Claro Que Subjuntivo O Indicativo

The indicative mood is the most common mood in Spanish and is used to state facts, express opinions, or describe events. It is used in independent clauses that stand alone and do not depend on another clause.
Examples of Indicative Mood Sentences
- El libro está sobre la mesa.(The book is on the table.)
- Creo que va a llover.(I think it’s going to rain.)
- Ayer fui al cine.(Yesterday I went to the movies.)
Distinguishing Subjunctive from Indicative
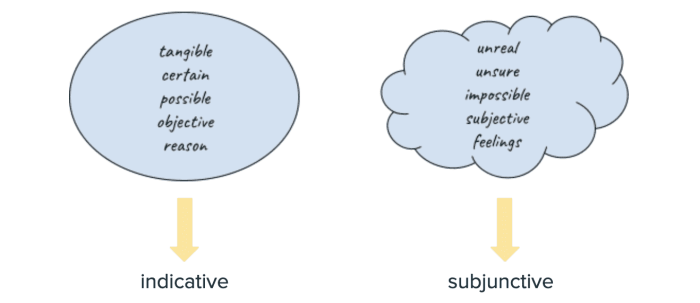
The subjunctive and indicative moods can be distinguished based on:
- Grammatical cues:Subjunctive verbs typically have different verb endings than indicative verbs.
- Context clues:The meaning of the sentence can indicate which mood should be used.
| Subjunctive | Indicative |
|---|---|
| Expresses uncertainty, doubt, or emotion | States facts, opinions, or describes events |
| Used in subordinate clauses | Used in independent clauses |
| Has different verb endings | Has regular verb endings |
Common Usage Scenarios
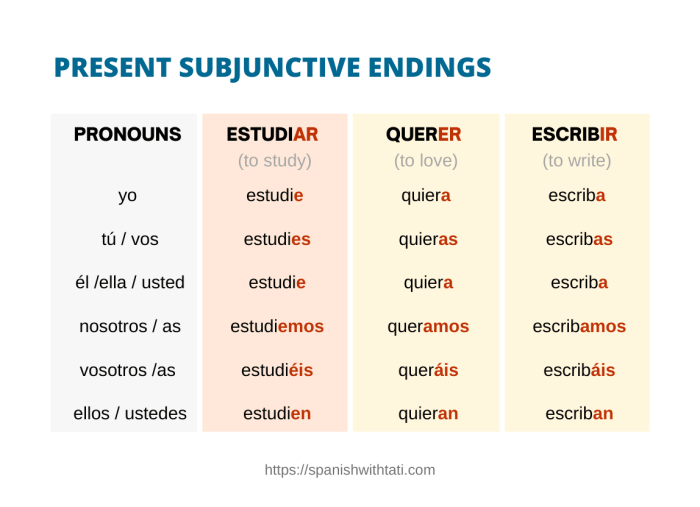
The subjunctive mood is commonly used in Spanish to express:
- Wishes and desires: Ojalá que llueva.(I wish it would rain.)
- Suggestions: Te sugiero que vayas al médico.(I suggest you go to the doctor.)
- Doubt and uncertainty: No creo que venga.(I don’t think he’s coming.)
- Emotions: Me alegro que estés bien.(I’m glad you’re okay.)
Detailed FAQs
What is the primary purpose of the subjunctive mood in Spanish?
The subjunctive mood is primarily used to express uncertainty, possibility, emotion, or hypothetical situations.
How can I differentiate between the subjunctive and indicative moods in Spanish?
The subjunctive mood often uses specific verb forms and is triggered by certain conjunctions or expressions that indicate uncertainty or subjectivity.
In what situations is the subjunctive mood commonly employed?
The subjunctive mood is frequently used in clauses expressing wishes, doubts, emotions, or hypothetical scenarios.